Share this Article

The Nepali diaspora refers to the millions of Nepali people who have migrated from Nepal to various parts of the world, forming vibrant communities in countries across Asia, Europe, North America, and beyond. As of recent estimates, the Nepali diaspora is one of the fastest-growing migrant groups globally, with significant populations in India, the United States, the United Kingdom, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. This widespread migration, driven by factors such as employment opportunities, political instability, and educational pursuits, has resulted in the development of tight-knit Nepali communities abroad. While these communities have thrived in their new homes, they face the unique challenge of maintaining their cultural identity while adapting to foreign environments.
1. Factors Driving Nepali Migration

The reasons for Nepali migration are varied, and they include:
- Economic Opportunities: One of the major drivers of migration is the search for better job prospects. Many Nepali workers have sought employment in the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and other parts of the world, often in sectors like construction, domestic work, hospitality, and healthcare. This economic migration has played a significant role in supporting families and communities back home.
- Education: The pursuit of higher education has also been a key factor for migration. Nepalese students have increasingly sought opportunities to study abroad, particularly in countries like the United States, Australia, Canada, and the United Kingdom. These students often face the challenge of balancing their academic pursuits with maintaining connections to their Nepali roots.
- Political Instability and Conflict: Periods of political instability, including the decade-long Maoist insurgency and other political upheavals, prompted many Nepali families to seek refuge and stability abroad, particularly in countries offering asylum.
- Family Reunification: Once family members establish themselves abroad, there is often a desire to reunite with loved ones, which further strengthens diaspora communities.
2. Challenges in Preserving Cultural Identity
While the Nepali diaspora has managed to carve out a space in foreign lands, the preservation of cultural identity remains a complex task. As Nepali communities settle into their new environments, they face several challenges:
- Assimilation and Integration: One of the most significant challenges for the diaspora is the pressure to assimilate into the culture of the host country. In countries like the United States and the United Kingdom, where there are significant cultural differences, Nepali immigrants often find themselves caught between maintaining their traditional customs and blending into the multicultural society they now live in.
- Generational Gaps: The second and third generations of Nepali immigrants, who grow up in foreign countries, may feel disconnected from their heritage. They are often more influenced by the dominant culture of their host countries, and their connection to Nepali traditions may be diluted. This can lead to a generational divide in cultural practices, language use, and lifestyle choices.
- Language Barriers: Language is a crucial aspect of cultural identity. Many first-generation Nepali immigrants continue to speak Nepali fluently, but their children may not. The loss of language among younger generations is a significant concern as it can lead to a weakening of cultural ties. Language is not just a tool for communication but also a way to preserve folklore, traditions, and history.
- Cultural Erosion: As the Nepali diaspora becomes more integrated into global culture, there is a risk of cultural erosion. Traditional customs, festivals, and practices may not be as easily practiced or celebrated in foreign lands, leading to a gradual loss of cultural heritage over time. Additionally, the convenience of modern technology and entertainment from other cultures may overshadow Nepali cultural practices.
3. Ways the Nepali Diaspora Maintains Cultural Identity
Despite these challenges, Nepali communities abroad have developed various strategies to maintain their cultural identity:
- Cultural Festivals and Celebrations: One of the most prominent ways that Nepali communities maintain their cultural identity is through the celebration of traditional festivals. Major festivals such as Dashain, Tihar, Holi, Maghe Sankranti, and Buddha Jayanti are widely celebrated within Nepali communities abroad. These festivals provide a sense of belonging and allow families to reconnect with their cultural roots. They also offer an opportunity for younger generations to learn about traditional practices, rituals, and Nepali values.
- Cultural Organizations and Community Centers: Many Nepali communities abroad have established cultural organizations or community centers. These centers play a critical role in organizing cultural events, festivals, language classes, and social gatherings. In cities with large Nepali populations, such as Kathmandu, New York, London, and Doha, these organizations provide a vital link to Nepali culture and help foster a sense of community. They serve as spaces for socializing, networking, and learning about Nepali arts, music, and history.
- Nepali Schools and Language Classes: To combat the loss of language, many Nepali communities abroad have set up language schools or language classes for children. These schools teach Nepali language, literature, and cultural studies. Children and young adults can learn how to read and write in Nepali, keeping the language alive for future generations. The teaching of Nepali folk songs, dances, and traditional arts is also common in these schools.
- Media and Entertainment: Nepali diaspora members often turn to Nepali media outlets, such as television channels, radio stations, and social media platforms, to stay connected with news, entertainment, and cultural programs from Nepal. Nepali-language films, music, and television shows, along with social media influencers, help keep the culture alive in a modern and accessible way. YouTube, in particular, has become a space for Nepali content creators to reach out to global audiences.
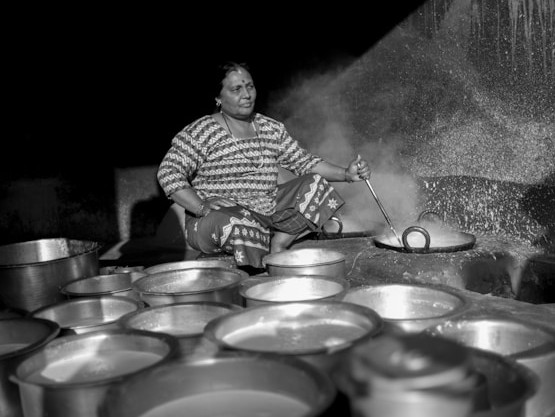
- Nepali Cuisine and Culinary Traditions: Food plays a significant role in maintaining cultural identity. Nepali families living abroad often recreate traditional dishes such as dal bhat, momo, sel roti, and gundruk. Nepali restaurants in foreign countries are also important cultural hubs, offering not only authentic food but also a space for the community to gather and share memories of home. Food is often an accessible way to keep cultural traditions alive, as it brings families and friends together and offers a taste of home.
- Religious Institutions: For many Nepali immigrants, religion is a central aspect of cultural identity. Nepali temples and religious centers abroad provide a space for prayer, worship, and community bonding. These institutions often serve as focal points for cultural and religious celebrations and create a sense of unity among people of similar faiths, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Christianity.
4. The Role of the Younger Generation in the Diaspora

The younger generation of the Nepali diaspora holds the key to maintaining and evolving cultural identity. While they may face challenges in connecting with traditional practices, many young Nepalis abroad are taking an active role in preserving their heritage:
- Cultural Fusion: Many young Nepali people are exploring ways to combine Nepali cultural elements with their host country’s culture. This fusion often manifests in the arts, fashion, and music. For instance, Nepali hip-hop, rap, and contemporary music are growing in popularity among younger generations, blending Nepali and global music trends. This fusion of traditional and modern influences helps the diaspora’s culture remain relevant and appealing to younger people.
- Activism and Advocacy: Many young Nepali individuals abroad are also involved in advocacy and activism, raising awareness of Nepali issues such as migration rights, environmental challenges, and social justice. This engagement with social issues allows them to stay connected to their Nepali roots while addressing issues of importance in their adopted countries.
- Cultural Entrepreneurship: Some young Nepali diaspora members are using entrepreneurship to maintain and share their cultural identity. They create businesses related to Nepali products, arts, and crafts, ranging from restaurants and clothing lines to media companies. These enterprises serve as cultural ambassadors, educating and introducing Nepali heritage to wider audiences.
5. The Future of Nepali Cultural Identity Abroad
The Nepali diaspora’s cultural identity will continue to evolve as future generations balance the desire to preserve traditions with the need to adapt to changing social, political, and technological landscapes. The role of technology, globalization, and education will be pivotal in shaping how Nepali culture is maintained and celebrated in the years to come. Ultimately, the Nepali diaspora’s ability to preserve cultural heritage while embracing new influences will ensure that Nepali identity remains vibrant, dynamic, and relevant in a globalized world.
Conclusion
The Nepali diaspora is a testament to the resilience of culture, identity, and community. While maintaining a connection to their heritage can be challenging, Nepali communities abroad have developed innovative ways to keep their culture alive through festivals, community organizations, language schools, media, cuisine, and religious institutions. The younger generation plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between tradition and modernity, ensuring that Nepali identity continues to thrive across borders. Through these efforts, the Nepali diaspora not only preserves its cultural roots but also contributes to the diversity of the global cultural landscape.
Categories:
Travel & Tourism
Tags:
nepali migration
,
diaspora