Share this Article
Introduction
Nepal, with its diverse geography, rich cultural heritage, and traditional healing practices, is home to an extensive array of medicinal herbs that have been used for centuries by indigenous communities. These herbs are not just crucial for health and wellness but are integral to Nepal’s spiritual and cultural identity. In rural areas, where modern healthcare facilities are sparse, traditional knowledge of herbal medicine is still relied upon. However, this knowledge is facing the risk of being lost due to urbanization, environmental changes, and the increasing dominance of modern medicine. Preserving the knowledge of Nepali medicinal herbs for future generations is crucial, both for safeguarding traditional healing practices and for sustaining biodiversity. This article explores the importance of medicinal herbs in Nepali culture, the role they play in healthcare, and the steps being taken to ensure their preservation.
The Richness of Nepali Medicinal Herbs
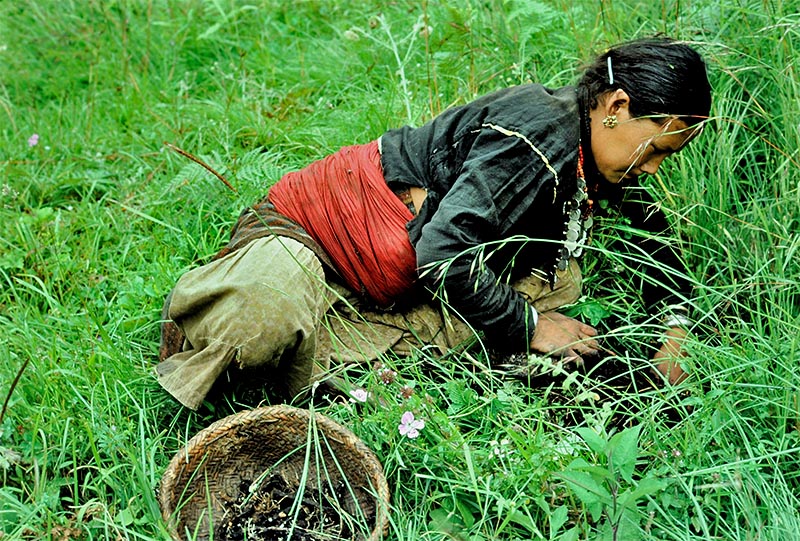
- A Diverse Flora for Healing Nepal’s unique topography, ranging from the lowland Terai plains to the towering peaks of the Himalayas, creates a wide variety of ecosystems. These environments harbor a diverse range of medicinal plants that are used in treating various ailments. Some of the most widely known medicinal herbs include:
- Yarsagumba (Cordyceps sinensis): Often referred to as the “Himalayan Viagra,” this fungus is used for its aphrodisiac properties and is believed to enhance energy levels, improve sexual function, and treat a variety of diseases.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): A powerful herb that is used to reduce stress, improve sleep, boost the immune system, and increase energy levels.
- Sarpagandha (Rauvolfia serpentina): Known for its use in treating high blood pressure and as a tranquilizer in mental health treatments.
- Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia): A well-known immune booster, used to treat fever, digestive disorders, and enhance overall health.
- Tulsi (Holy Basil): Revered for its antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties, this herb is used to treat respiratory infections, cough, and fever.
- Aloe Vera (Aloe barbadensis): Used for treating skin conditions, burns, and digestive issues.
- Yarsagumba (Cordyceps sinensis): Often referred to as the “Himalayan Viagra,” this fungus is used for its aphrodisiac properties and is believed to enhance energy levels, improve sexual function, and treat a variety of diseases.
- Traditional Use and Preparation In Nepal, medicinal herbs are often prepared in various forms, such as decoctions, pastes, powders, and oils. They are combined with other herbs or ingredients to enhance their potency or address a specific health issue. For example, Yarsagumba is typically used in a tonic form, mixed with ghee or milk, while Ashwagandha is consumed as a powder or in herbal teas. In many villages, traditional healers, often known as Vaidyas or Jhankris, prepare herbal remedies and offer guidance on their use.
- Cultural Significance The use of medicinal herbs in Nepal is deeply intertwined with cultural and spiritual practices. For centuries, Nepali people have relied on these herbs not only for physical healing but also for their spiritual and emotional well-being. Many of these herbs are considered sacred and are used in religious ceremonies or during auspicious events. For instance, Tulsi is often planted near homes as a way to purify the environment and promote well-being. The ritual use of medicinal herbs goes hand in hand with the spiritual worldview of the Nepali people, where the mind, body, and spirit are seen as interconnected.
Challenges in Preserving Traditional Knowledge
- Loss of Traditional Wisdom As modern medicine and technologies become more accessible, traditional knowledge about medicinal herbs is slowly being forgotten, especially in urban areas. The younger generation, in particular, is less interested in learning the ancient practices from elders. With the globalization of health and wellness trends, synthetic alternatives have also started to overshadow herbal remedies, leading to a decline in the demand for traditional herbal medicines.
- Environmental Degradation Nepal's rich biodiversity is under threat due to climate change, deforestation, and over-harvesting of medicinal plants. Many of the herbs that are used in traditional healing practices are found only in specific regions of Nepal, often in the high altitudes of the Himalayas. As global warming affects these ecosystems, the habitats for these plants are shrinking, which leads to a reduction in the availability of medicinal herbs. Over-harvesting, often driven by market demand, further exacerbates this issue.
- Commercialization and Standardization The commercial exploitation of medicinal plants, both within Nepal and internationally, has led to a loss of cultural context and traditional knowledge. While some herbs are now being cultivated in controlled environments, the indigenous methods of harvesting, preparation, and application are often not followed, leading to a diluted or improper use of these plants.
Efforts to Preserve Nepali Medicinal Herb Knowledge
- Documentation and Research There have been concerted efforts to document traditional knowledge related to medicinal herbs. Local communities, herbalists, and researchers are collaborating to record ancient remedies and their applications in modern contexts. This information is being digitized and preserved for future generations. Universities and research institutions in Nepal are conducting scientific studies to validate and understand the medicinal properties of these plants, providing a bridge between traditional knowledge and modern healthcare practices.
- Conservation of Biodiversity There are several initiatives underway to protect the native habitats of medicinal herbs in Nepal. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs), governmental bodies, and local communities are working together to create protected areas and implement sustainable harvesting practices. In some areas, medicinal plant gardens and nurseries are being established to cultivate and conserve endangered plants, reducing the need for wild collection.
- Herbal Education and Training Many indigenous healers are now participating in programs designed to pass on their knowledge to the younger generation. Training programs that focus on sustainable herbal practices, ethical harvesting, and preparation methods are helping to preserve this ancient wisdom. Some schools and universities in Nepal are introducing courses on herbal medicine and traditional healing practices to ensure that the knowledge is passed on to future generations.
- Promoting Ecotourism In many parts of Nepal, particularly in the Himalayas, there is a growing interest in ecotourism. This form of tourism emphasizes the preservation of nature and cultural heritage. Tourists are encouraged to learn about traditional herbal medicine, and some tours even offer workshops on the identification and use of medicinal herbs. This not only supports the conservation of these plants but also provides an economic incentive for local communities to protect their natural resources.
The Future of Nepali Medicinal Herbs
The future of Nepali medicinal herbs depends on the continued preservation of traditional knowledge and the protection of the natural habitats in which these plants grow. A balanced approach that combines the wisdom of indigenous practices with modern scientific research will ensure that these herbs continue to play a vital role in healthcare for generations to come. Additionally, the growing interest in natural and holistic health solutions worldwide presents an opportunity to revitalize the use of Nepali medicinal herbs both locally and internationally.
The preservation of these plants and practices will also help safeguard Nepal’s cultural heritage, providing a link to the spiritual, ecological, and medicinal practices that have sustained Nepali communities for centuries. As the world increasingly turns to sustainable and natural alternatives to modern medicine, Nepali medicinal herbs could play a critical role in global health.
Conclusion
Nepali medicinal herbs have a deep-rooted place in the country’s culture and healthcare systems. The preservation of these herbs, along with the traditional knowledge that accompanies them, is essential for maintaining a link to the past while securing the health and well-being of future generations. By combining efforts to conserve biodiversity, protect the environment, and promote sustainable practices, Nepal can ensure that the healing power of its plants will continue to benefit both its people and the wider world.
Categories:
Medicinal Plants of Nepal
Tags:
Ayurveda
,
herbs